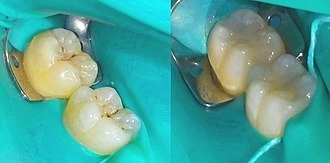
Are you wondering what resin-based composites are and why they’re so popular in dentistry and industry? Choosing the right materials can transform dental restorations or industrial projects, and understanding resin-based composites is key to making informed decisions.
As a trusted supplier, Blissam knows the ins and outs of these versatile materials. In this guide, we’ll break down the composition, uses, and benefits of resin-based composites, drawing on industry expertise to give you practical insights.
Whether you’re a patient curious about composite fillings or a professional exploring industrial applications, this article has you covered. Let’s dive in!
What is Resin-Based Composite
A resin-based composite is a versatile material composed primarily of a resin matrix combined with inorganic fillers, used widely in both dental and industrial fields. In dentistry, it is famously known as dental composite resin or composite fillings, playing a crucial role in restorative procedures such as dental restorations. These composites offer a balance of aesthetics and mechanical strength, making them an essential material in modern treatments.
Definition
Resin-based composites are synthetic materials formed by blending a resin matrix, usually made from monomers like Bis-GMA (bisphenol A-glycidyl methacrylate), with inorganic fillers such as silica or glass particles. This combination provides a material that is both durable and moldable, capable of adhering closely to natural tooth structures or other substrates.
Key Components
The performance and properties of resin-based composites depend largely on their components:
- Resin Matrix: Typically includes Bis-GMA or related methacrylate-based monomers, which form the base and enable polymerization.
- Inorganic Fillers: These microscopic particles enhance strength, reduce polymerization shrinkage, and improve wear resistance. Fillers vary from micron-sized particles to advanced nanohybrid composites.
- Photoinitiator: A chemical agent that triggers curing when exposed to a specific light source, allowing precise control over the setting process.
- Optional additives such as pigments for color matching and bioactive components that promote tooth remineralization.
How Resin-Based Composites Work
The setting process involves polymerization, where the resin matrix undergoes a chemical reaction—usually initiated by light—causing the material to harden and bond securely to tooth surfaces or industrial components. This curing can be controlled by varying light intensity, exposure time, and photoinitiator concentration. The inorganic fillers not only strengthen the cured composite but also reduce shrinkage, a common drawback in earlier formulations.
Understanding this mechanism clarifies why precise formulation and curing techniques are vital to achieving optimal results in applications like composite fillings and other types of repairs.
For more insight into how resin cures and its practical handling, you can explore additional resources such as What is Cured Resin to better understand the chemistry behind these materials.
Applications of Resin-Based Composites in Dental and Industrial Fields
Resin-based composites are widely used because they combine strength, aesthetics, and versatility. Let’s break down their main applications in both dental and industrial sectors.
Dental Applications of Resin-Based Composites
In dentistry, dental composite resin is a go-to material for many types of dental restorations. Here’s why it stands out:
- Composite Fillings: Most commonly used for tooth-colored fillings, these composites replace traditional metal amalgams. They blend seamlessly with natural teeth and are preferred for both front and back teeth.
- Restorative Treatments: Used in repairing chipped, cracked, or decayed teeth.
- Bonding and Veneers: Resin composites help in cosmetic procedures, improving the shape and color of teeth.
- Nanohybrid Composites: These newer versions enhance strength and polishability, making restorations longer-lasting and more resistant to wear.
- Polymerization and Curing: A photoinitiator in the resin matrix allows it to harden quickly under special light, speeding up treatments.
Dentists favor these composites because they are minimally invasive and preserve more of the natural tooth structure compared to other materials.
Industrial Applications of Resin-Based Composites
Beyond dentistry, resin-based composites are valuable in various industries because of their durability and lightweight properties:
- Construction and Manufacturing: Used in producing durable parts that require strength without added weight, such as in automotive or aerospace components.
- Electronics: Resin composites serve as insulators or protective coatings due to their chemical stability and resistance to moisture.
- Marine and Sports Equipment: Their resistance to corrosion and impact makes them ideal for boat parts, helmets, and other gear.
In these industrial roles, composites often feature a mix of inorganic fillers to enhance mechanical and thermal properties. Their adaptability allows manufacturers to customize the strength, flexibility, and appearance of the final product.
of Key Applications
| Sector | Common Uses | Important Features |
|---|---|---|
| Dental | Composite fillings, bonding | Tooth-colored, quick curing, durable |
| Industrial | Automotive parts, electronics | Lightweight, strong, corrosion-resistant |
Understanding these applications helps you select the right resin-based composite based on your specific needs, whether for restoring smiles or building high-performance industrial products.
Benefits of Resin-Based Composites in Dental Restorations and Beyond
Resin-based composites offer several key advantages that make them a popular choice, especially in dental applications but also across various industries.
Aesthetic Appeal and Natural Look
One of the biggest benefits of dental composite resin is its ability to closely match the natural color of teeth. This makes composite fillings ideal for visible areas, allowing for more discreet and attractive dental restorations compared to traditional metal fillings.
Strong and Durable with Flexibility
Thanks to their mix of resin matrix and inorganic fillers, these composites are both strong and flexible. This balance means they can handle the daily forces of chewing while also bonding tightly to tooth structures, providing lasting performance without easily cracking or breaking.
Conservative Treatment
Using resin-based composites often means dentists can preserve more of the natural tooth. Unlike some materials that require removing healthy parts, composites allow for less invasive treatments, keeping your tooth structure intact.
Versatility Across Applications
While most well-known for dental uses, resin-based composites also serve industrial purposes such as coatings, adhesives, and moldings. Their adaptability to different formulations lets manufacturers customize strength, durability, and appearance.
Quick and Easy Application
Composite fillings are cured rapidly with a photoinitiator and a dental curing light, minimizing chair time for patients. This efficient polymerization process helps reduce discomfort and speeds up treatment.
Biocompatibility and Safety
Modern composites, especially bioactive composites, are designed to be safe and gentle on tissues. Many formulations reduce the risk of irritation or allergic reactions, making them suitable for a wide range of patients.
Cost-Effective Long-Term Solution
Though sometimes pricier upfront than amalgam fillings, the long-term performance and appearance of resin-based composites often translate into fewer replacements or repairs, saving money over time.
By choosing resin-based composites, you’re getting a material that blends look, strength, safety, and ease — meeting the specific needs of both dental patients and industrial users across the US market.
Drawbacks and Considerations of Resin-Based Composites
While resin-based composites like dental composite resin offer great benefits, it’s important to understand their drawbacks and key considerations before choosing them for dental restorations or industrial uses.
Polymerization Shrinkage
One significant issue is polymerization shrinkage. When the resin hardens (especially in dental fillings), it can shrink slightly. This shrinkage may cause:
- Gaps between the filling and tooth
- Increased risk of sensitivity or leakage
- Potential for secondary decay
Wear and Longevity
Compared to traditional materials like amalgam, resin composites might wear down faster under heavy chewing forces. This means:
- Composite fillings may need replacement more often
- In high-stress areas, composites might not last as long without careful material selection
Technique Sensitivity
Applying resin-based composites requires precise technique, including:
- Proper layering and curing with a photoinitiator using a curing light
- Avoiding contamination from moisture or saliva during placement
Poor technique can lead to weaker restorations or bonding failures.
Staining and Color Stability
Although composites are designed to blend with natural teeth, they can stain over time from foods, drinks, or smoking. This may require polishing or replacement to maintain appearance.
Cost Factors
Resin composites tend to be more expensive than some traditional materials, especially when considering:
- Professional application time
- Specialized light-curing equipment
- Use of advanced materials like nanohybrid composites or bioactive composites
Biocompatibility and Allergies
While rare, some patients may react to components like Bis-GMA or other resin matrix chemicals. Consider patient history and sensitivity when choosing materials.
In , resin-based composites deliver excellent aesthetics and functionality but require awareness of shrinkage, technique, wear, and costs. Careful material selection and application ensure the best results for dental restorations or industrial uses.
Recent Advancements in Resin-Based Composites
Resin-based composites have seen significant improvements recently, driven by the demand for better performance in both dental and industrial applications. These advancements focus on enhancing durability, aesthetics, and bioactivity while minimizing common issues like polymerization shrinkage.
Enhanced Filler Technology
Modern composites use nanohybrid composites that blend nano-sized inorganic fillers with traditional particles. This results in:
- Improved strength and wear resistance
- Better polishability for dental restorations
- Increased longevity of composite fillings
The smaller filler particles help maintain a smoother surface, making dental composite resin closer in appearance to natural teeth.
Improved Resin Matrix Formulations
Researchers have optimized resin matrices by incorporating Bis-GMA and other resin monomers with novel additives. These formulations offer:
- Reduced polymerization shrinkage, which lowers stress on the bonded tooth or substrate
- Enhanced flow and handling properties for easier application
- Increased resistance to discoloration and degradation over time
This not only improves clinical outcomes but also extends the life span of resin-based composites in varied environments.
Introduction of Bioactive Composites
Bioactive composites are a breakthrough, especially in dental materials. They can:
- Release beneficial ions like calcium and phosphate
- Promote remineralization of tooth structures
- Offer antibacterial properties to reduce recurrent decay
By integrating bioactive components, these composites add not just mechanical strength but also healing potential to dental restorations.
Smart Photoinitiators
Advances in photoinitiator systems now allow for more efficient curing with less light exposure. Benefits include:
- Faster polymerization with lower heat generation
- Deeper curing in thicker layers of composite fillings
- Reduced risk of incomplete curing, enhancing mechanical performance
These innovations make dental procedures quicker and composites more reliable.
Customizable and Functional Resins for Industry
On the industrial side, developments include new silicone-resin blends and methyl-phenyl silicone resin formulations that improve thermal stability, flexibility, and chemical resistance. These materials offer:
- Better adhesion and durability in harsh conditions
- Adaptability for coatings, adhesives, and mold-making applications
For more on silicone-resin blends, you can check out our detailed chemical options.
These recent advancements make resin-based composites more versatile, durable, and biocompatible, meeting the evolving needs of dental professionals and industrial users in the United States market.
How to Choose the Right Resin-Based Composite for Your Needs
Selecting the right resin-based composite is vital, whether you’re working in dentistry or industrial applications. The market offers a variety of options, so here’s how to narrow down your choice effectively.
Understand the Purpose and Application
- Dental restorations: Choose composites like nanohybrid composites or bioactive composites that offer strength, aesthetics, and minimal polymerization shrinkage for fillings and bonding.
- Industrial uses: Look for composites with specific resin matrices and inorganic fillers tailored for durability and environmental resistance.
Consider Key Components
- Resin matrix type: Materials like Bis-GMA are common in dental composites and impact physical properties such as hardness and wear resistance.
- Inorganic fillers: Higher filler content typically means better strength and less shrinkage but may affect handling.
- Photoinitiator system: For dental composite resin applications, ensure compatibility with curing lights to achieve proper polymerization.
Evaluate Performance Factors
- Strength and durability: Essential for long-term use, especially in dental composite fillings under chewing pressure or in industrial manufacturing.
- Aesthetics: For visible dental restorations, pick composites that blend well with natural tooth color.
- Handling and work time: Composites should be easy to shape and place before curing.
- Shrinkage and wear resistance: Lower polymerization shrinkage reduces gaps and post-treatment sensitivity.
Check Compatibility and Safety
- Verify that the composite complies with US regulations and industry standards.
- If using for dental purposes, confirm biocompatibility and non-toxicity.
- For industrial applications, make sure it fits with existing equipment and process conditions.
Seek Latest Innovations
- Consider bioactive composites that promote healing and bond better.
- Nanohybrid composites offer an excellent balance of strength and esthetics.
- Stay updated on products minimizing shrinkage and improving longevity.
Final Tips for Selection
- Consult with professionals or suppliers to match composites with specific tasks.
- Request samples or trials to test handling and curing performance.
- Review technical sheets focusing on filler load, resin type, and curing recommendations.
By focusing on these criteria, you can choose the right resin-based composite that fits your exact needs, ensuring reliability, performance, and value in both dental and industrial contexts.